In the Neurology Department the highly qualified specialists provide complex diagnostics and treatment of acute and chronic diseases and functional disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system. The department annually provides diagnostics and treatment more than 2,000 patients on inpatient and more than 5,000 patients on outpatient base.
In its diagnostic and therapeutic activity the Department of Neurology is working closely with the specialized departments of diagnostics, neurosurgery, neuroangeology, spine pathology, physiotherapy and rehabilitation, et al.
In the frame of the Department of Neurology operate specialized services such as:
 |
Service of Neuromuscular Disorders Treatment - Head Armine Kteyan | ||
 |
Service of Sleep Disorders Treatment - head Samson Khachatryan | ||
 |
Service of Movement Disorders Treatment - Head Zara Tavadyan |
 In the department of neurology is introduced the contemporary approaches for treatment regimens neurological diseases recommended by the International Association of Neurologists.
In the department of neurology is introduced the contemporary approaches for treatment regimens neurological diseases recommended by the International Association of Neurologists.
Medical personnel of the department is involved in various scientific conferences and symposia on modern neurology, constantly improving their qualification, knowledge and skills.
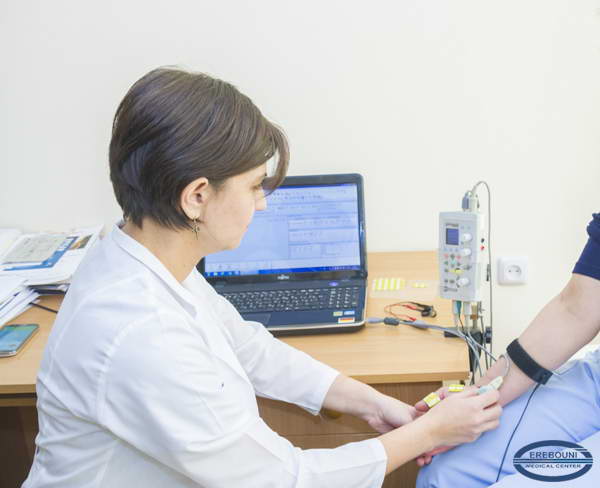
Service of Neuromuscular Disorders Treatment provides diagnoses and treatment of about 100 patients per month with a variety of neuromuscular diseases, including neuropathy (axonal and demyelinating), radiculopathy, myopathies and disorders of neuromuscular synapses. Department is equipped with electroneuromyography, which serves the patients from neurological and neurosurgery, rheumatology, endocrine, orthopedic departments of MC Erebouni.
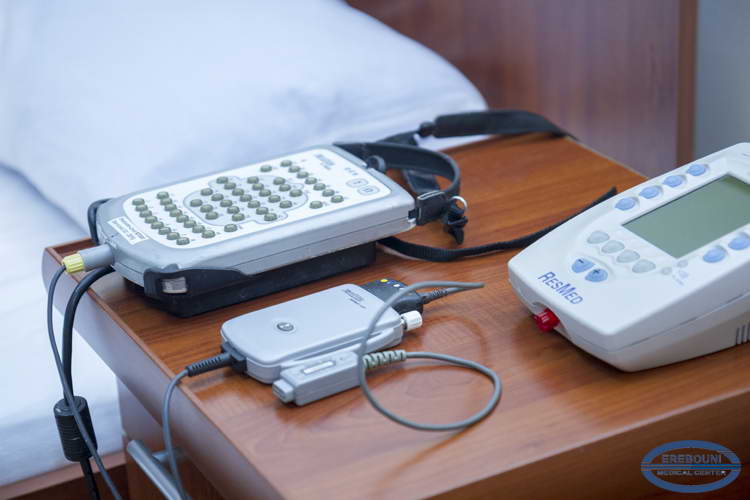
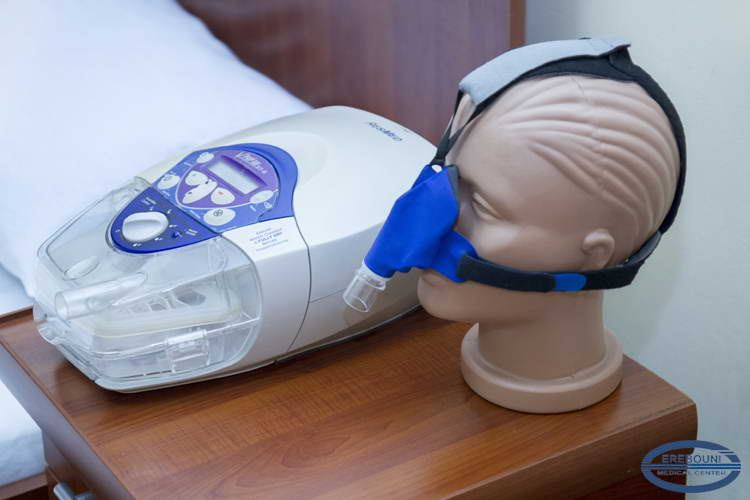
Service of Sleep Disorders Treatment operates on the basis of Somnos Center of sleep disorders that deployed in MC Erebоuni. The service provides diagnosis and treatment of all types of sleep disorders, including insomnia (insomnia), respiratory disorders during sleep, particularly apnea, motor disorders during sleep, as well as the problems of excessive sleepiness (hypersomnia, narcolepsy), parasomnias and sleep circadian rhythm disorders. Today about 700 patients stays at regular medical check-up of the Center. For the diagnosis of sleep disorders are used as questionnaires, MSLT and MWT tests (for the diagnosis of daytime sleepiness) and hardware diagnostic methods: polysomnography, motor printing, actigraphy. Diagnosis and treatment of patients is carried out by professionals who have advanced training in clinics of US and Europe
Sleeplessness (insomnia) is a sleep disorder, which is characterized by insufficient length or poor quality of sleep, or a combination of these phenomena over a significant period of time, causing the deterioration of daily activities.
Breathing disorders during sleep. The most common species is nocturnal snoring and apnea (cessation of breathing) during sleep. Sleep apnea is a kind of sleep apnea, which is characterized by cessation of pulmonary ventilation during sleep for more than 10 seconds. Most often, it takes 20-30 seconds, although in severe cases, can reach 2-3 minutes and take up 60% of the total time of a night's sleep. With regular apnea (typically at least 10-15 times per hour) there is sleep apnea syndrome with disruption of the structure of sleep and daytime sleepiness, memory and intellect impairment, complaints to the decreased performance and constant fatigue, depression. There are obstructive and central sleep apnea, as well as their mixed forms. The cause of sleep apnea is a collapse of the throat tissue, resulting in a narrowing of the upper airway during sleep, followed by a decrease in blood oxygen accompanied by hypoxia and hypercapnia with metabolic acidosis.
 Hypersomnia and narcolepsy. Hypersomnia is a phenomenon when a person needs a pathologically increased amount of sleep. Healthy people, depending on the characteristics of the organism require 5 to 10 hours of sleep a day, and the amount varies greatly depending on their activity type. Average of sleep duration in healthy people in normal work schedule varies from 7 to 9 hours. In everyday life it is a little less than a weekend. In hypersomnia or very strong drowsiness the episodes of sleep may occur during day and it will disrupt the normal human being, and may even threaten his life. Various pathological variants of hypersomnia called narcolepsy.
Hypersomnia and narcolepsy. Hypersomnia is a phenomenon when a person needs a pathologically increased amount of sleep. Healthy people, depending on the characteristics of the organism require 5 to 10 hours of sleep a day, and the amount varies greatly depending on their activity type. Average of sleep duration in healthy people in normal work schedule varies from 7 to 9 hours. In everyday life it is a little less than a weekend. In hypersomnia or very strong drowsiness the episodes of sleep may occur during day and it will disrupt the normal human being, and may even threaten his life. Various pathological variants of hypersomnia called narcolepsy.
Parasomnias is occurring during sleep abnormal episodic condition: sleepwalking (somnambulism), sleep speaking, night fear (nightmares), night horrors (terrifying dreams), nocturnal heart rhythm disorders, sleep apnea syndrome, congenital central hypoventilation syndrome, teeth-grinding (bruxism) and others. The origin of these disorders is mainly psychogenic.
Restless legs syndrome is a condition characterized by unpleasant sensations in the lower limbs, which appear at rest and forcing the patient to move the legs and often lead to sleep disorders. More frequently it occurs in women. Often it is necessary to differentiate this disorder from the vascular disease of the lower extremities.
Sleep circadian rhythm disorders is a violation of the regularity of the "sleep-wake" cycle because of the de-synchronization of external and internal clocks. The patients has night sleep disorders, abnormal daytime sleepiness, or its combination, which usually take place because the biological clock rearranged themselves.
Service of Movement Disorders Treatment
 Movement disorders are usually divided into akinetic-rigid form, in which there is muscle stiffness and lethargy of movements, and hyperkinetic forms in which there are unconscious movements. In both cases, the muscle strength is maintained. Typically, movement disorders develop due to malfunction of neurotransmitters in the basal ganglia. The pathogenesis in this case may be different. Key factors are degenerative pathology (congenital or acquired), often resulting from the use of drugs, disrupt organ systems, an infection of the central nervous system, or ischemia of the basal ganglia.
Movement disorders are usually divided into akinetic-rigid form, in which there is muscle stiffness and lethargy of movements, and hyperkinetic forms in which there are unconscious movements. In both cases, the muscle strength is maintained. Typically, movement disorders develop due to malfunction of neurotransmitters in the basal ganglia. The pathogenesis in this case may be different. Key factors are degenerative pathology (congenital or acquired), often resulting from the use of drugs, disrupt organ systems, an infection of the central nervous system, or ischemia of the basal ganglia.
Bradykinesia is man's inability to initiate or carry out normal habitual movements. There is confusion and reduction of the number of automatically committed movements, such as swinging arms while walking, winking. In most cases, bradykinesia is a symptom of Parkinson's disease.
Tremor is rhythmic swing of the limbs or torso relatively to a certain point. As a rule, there is a tremor of the hands and feet, sometimes the head or lower jaw. Tremor can be classified by type based on the location and amplitude of oscillation. Large-swinging tremor usually makes 5 muscular tensions in the second (at rest), which indicates to parkinsonism. Kinetic (promotional) tremor with a frequency of 9-10 muscular tensions in the second may be a physiological tremor, or be a symptom of essential (familial) tremor caused by genetic factors.
Asterixis is abrupt arrhythmic movements, that interrupt the background involuntary muscle tension (usually it is a rapid movements of the hands). This symptom is observed in disorders of the liver functions, drug encephalopathy, a disorder of the work of certain organ systems or infection of the central nervous system. The first step is to treat the pathology that cause the tremor.
Myoclonus is quick arrhythmic muscular tension or twitching. As asterixis, myoclonus may be as a results of drug encephalopathy; sometimes it appears after the temporary cardiac arrest, when the total oxygen starvation of the brain provokes multifocal myoclonus.
Listania is involuntary prolonged static posture or abnormal postures. They are often absurd, unnatural, a forcible bending or straightening in certain joints. Dystonia is usually generalized or focal (cervical dystonia, blepharospasm).
Choreoathetosis is jointly processing chorea (irregular, jerky movements) and athetosis (slow, involuntary convulsive movements). These two motor disorders accompany each other, although one of the symptoms may be more pronounced. Chorea dominates in choreic dementia disease (disease of Sydenham) and Huntington's disease. Athetosis more pronounced in certain types of cerebral palsy. Long-term use of antipsychotics can cause dyskinesia, involving the muscles of the face, tongue and lower jaw.
Tic (convulsions) is stereotyped, involuntary movements like blinking, sneezing or coughing. May indicate to presence of Tourette's disease. Among the symptoms of this disease: motor tics (spasms of muscle of the face, neck), head tics (grunts, vocal tics), abnormal behavior (coprolalia, echolalia). Cause of the disease is not fully understood.
Upon detection of movement disorders for success of the treatment the patients should obtain timely consultation of the specialists that will allow beginning of the treatment on early stages of diseases.
At the department is functioning:
- Electrophysiology Laboratory, where carried out baseline EEG sleep deprivation EEG and EEG monitoring of the patients suffering from epilepsy, and various convulsive states, dementia and encephalopathy to make an accurate diagnosis
- Laboratory of electroneuromyography to diagnose diseases of the peripheral nervous system.
- sleep laboratory with the possibility of polysomnography in patients with obstructive apnea, insomnia and narcolepsy
- intensive care wards with central oxygen supply and the possibility of individual monitoring of 6 patients simultaneously
For qualitative examination and accurate diagnosis of neurological patients is also used modern diagnostic equipment of the Diagnostic Clinic of MC Erebouni
- CT scan of the brain, spine,
- angiography of the brain and neck,
- Doppler blood vessels of the brain and neck,
- Duplex scanning of vessels of the neck and head,
- diagnosis of cerebrospinal fluid,
- ultrasonic methods of examination,
- X-ray,
- X-ray densitometry,
- clinical and laboratory studies,
- neuro-ofthalmological examination
The department provides the treatment of following disease
 |
vascular disease of brain and spinal cord | |
|
||
 |
inflammatory diseases of the nervous system | |
|
||
 |
multiple sclerosis, | |
 |
peripheral nervous system diseases | |
|
||
 |
neuromuscular disease | |
 |
traumatic diseases of the central nervous system, | |
 |
epilepsy | |
 |
headaches, | |
 |
facial pain, | |
 |
degenerative /dystrophic diseases of the spine | |
|
||
 |
various neurological disorders that have arisen during the period of somatic diseases. | |


