Empyema is a collection or gathering of pus within a naturally existing anatomical cavity or in the confined space of the uterus. Empyema must be differentiated from abscess, which is situated in thick tissues and lined by pyogenic membrane. In empyema the purulent cavity is lined by mucosal, serous and synovial membrane.
Through prolonged and severe inflammation, mucosal (serous or synovial) membrane, lining organ or cavity, is partially or completely destroyed. In inflammation process are engaged the surrounding tissues with destruction and replacement them by granulation tissue. The clinical picture is defined by localization of inflammatory process, the local manifestation of the diseases and common purulent intoxication. The diagnosis is based on the data of clinical and special methods of investigations.
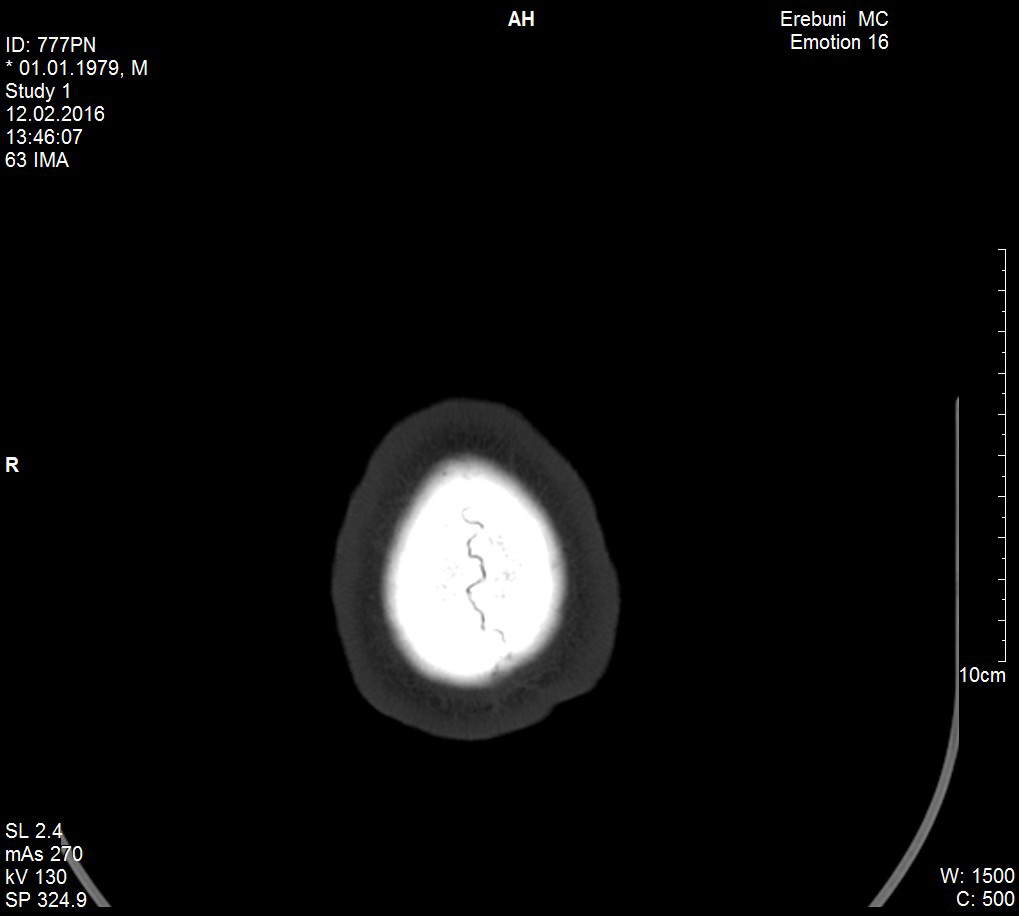
Patient P.V., 1979 y/b was admitted to MC Erebouni in 12.02.16 in critical condition: unconscious, with convulsions and purulent nasal discharge. The patient had fever 38,5-39◦ C.
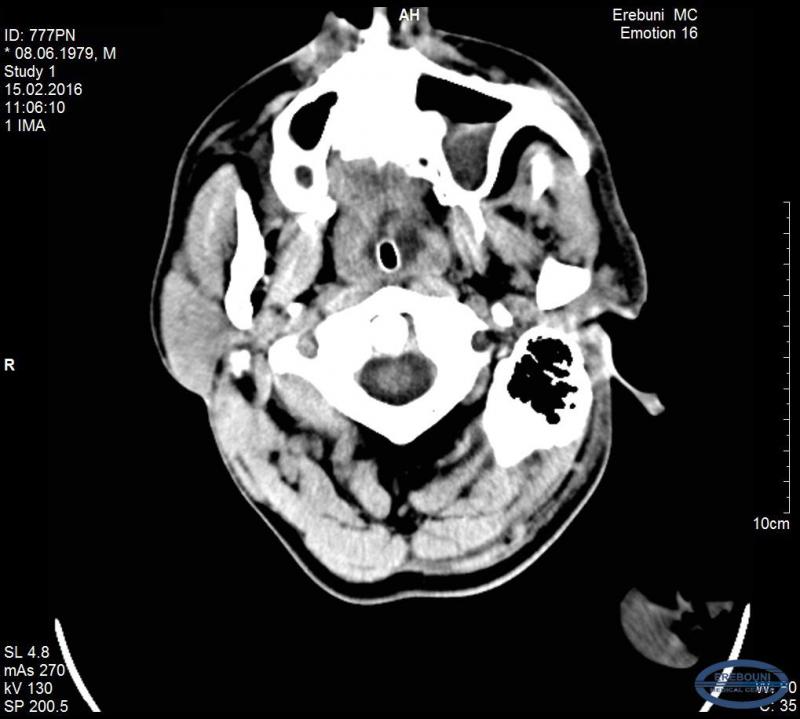
Before admission to MC Erebouni, the patient had suffered from headaches for 10 days and therefore consulted the doctor. It was diagnosed sinusitis, and the patient received proper therapy, which unfortunately was ineffective. The condition of the patient gets worse and he was taken to MC Erebouni where was made preliminary clinical diagnosis: Epidural hematoma. Abscess. Sinusitis.
After carrying out clinical and diagnostic investigations, on the basis of objective data, it was diagnosed: subdural empyema in the left parietal-temporal region of the head. Acute purulent sinusitis left frontal sinus mucocele, deviated septum. Mentioned pathological disorders were the basis for carrying out urgent surgical interventions.
On the same day 12.02.16 under general anesthesia the removal of subdural empyema in the left parietal-temporal region through extended burr hole was performed under the direction of the Head of ENT Department Dr. Shukuryan A.K., and Professor and the Head of Neurosurgery Department Dr. Hambardzumyan V.G. (MD,PhD).
Postoperative condition went smoothly. The control CT scan was carried out on the third day: the positive dynamics has been observed, and then one of the silicone tubes was removed. The liquor was flowed from the tube, which was left in the subdural space. The second silicone tube from the mentioned space was removed on the next day as well as the drainage tubes. There were also removed the drainages from the frontal sinus to nasal cavity.
The consciousness of the patient regained on the 5-6th day. The fever (which was observed at admission in postoperative period began to drop. The patient continues the treatment in Neurosurgical Department.
It is important to state that when a purulent sinusitis with formation of subdural empyema is detected, it is necessary to remove both subdural empyema and its original source-purulent sinusitis at the same time for avoiding relapse.
The experience of using the system with dioxidin and adequate bacterial therapy (taking into account indicators of bacterial seeding), which is used both in neurosurgical and in ENT Department of MC Erebouni during surgical interventions in empyemas had indicates that the given technique is the most acceptable and necessary, and the results in most cases lead to the treatment of the patient.