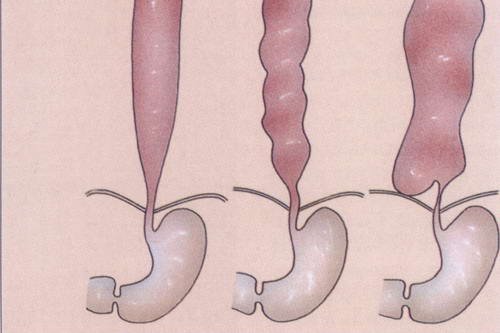
Achalasia of Esophagus is neurogenic disease of the lower esophageal sphincter, in which it is partially or completely loses the ability to relax in the process of swallowing. In achalasia the esophageal motility is violated, the tonus is decreased and cardiac sphincter partially or totally loses its ability to reflexive opening. It is believed, that the cause of the disease is a mismatch between neural mechanisms of regulation that responsible for the esophageal peristalsis and the work of its lower sphincter. In the constriction area the inflammatory degenerative and scar processes are formed, the wall is changed, losing its full function.
Two types of treatment are applied: conservative (medicine), and in case of its inefficiency, surgical treatment is applied. The use of medicine in esophageal achalasia is of secondary importance, the primary are surgical and some other methods of correction.
The aim of the treatment of achalasia is the improvement of the patency of the lower esophageal sphincter. To achieve this use of different medicine, balloon dilatation of the esophageal sphincter, injection of botulinum toxin into the sphincter or its surgical dissection is applied. The choice of the method of treatment of the disease depends on the stage of disease, the age of the patient, concomitant diseases, esophagus condition and some other factors.
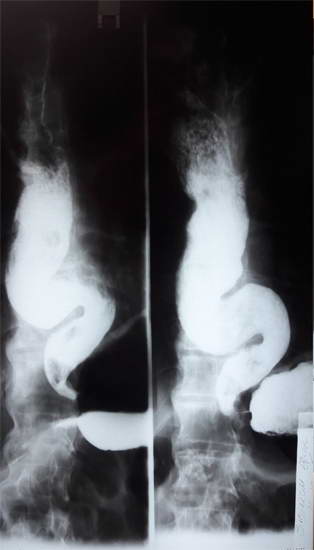
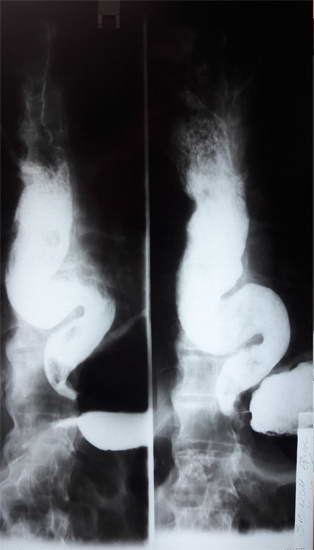
A patient S.E. 65-years-old, has been admitted to General Surgery Department of MC Erebouni and examined in the clinic since 12.10.2015, with chronic dyspeptic complaints; by esophagogastroduodenoscopy it is revealed significant dilation of the esophagus up to its abdominal part: the insertion of endoscope into the stomach has been failed. X-ray contrast study – esophageal achalasia, the 4th stage, (X-ray images (Fig. 1, 2,), after an hour – a partial emptying of contrast (Fig.3,4). ECG, blood test shows minor changes.
Pic. - 1 Pic. - 2
Pic. - 3 Pic. - 4
In 20.10.15 under the management of the Head of General and Thoratic Surgery Department Dr. A.R. Asatryan (MD) the surgical intervention was carried out: after saggital diaphragmotomy the esophageal hiatus is mobilized and somehow extended, abdominal esophagus mobilized, cardiac and fundal part of the stomach are mobilized, resected and modified the part of esophagus with cardiac sphincter of the stomach. Transhiatal esophago-gastro-anastomosis with fundoplication was performed. Heineke-Mikulicz piloroplasty was also carried out.
Post-operative period proceeded satisfactorily. The patient will be re-examined in a month.